filmov
tv
Isomerism | Types of Isomerism | Organic Chemistry

Показать описание
Link to buy the following products:
Different forms of the same molecule are known as structural isomers; they have the same molecular formula but are different 'shapes'.
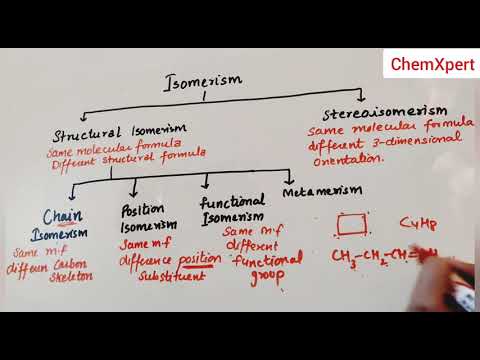
Isomerism is the phenomenon in which more than one compounds have the same chemical formula but different chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formulae but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers.
There are two primary types of isomerism, which can be further categorized into different subtypes. These primary types are Structural Isomerism and Stereoisomerism.
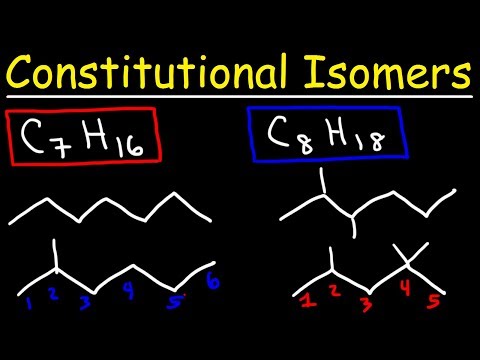
Structural Isomerism
Structural isomerism is commonly referred to as constitutional isomerism. The functional groups and the atoms in the molecules of these isomers are linked in different ways. Different structural isomers are assigned different IUPAC names since they may or may not contain the same functional group. The different types of structural isomerism are discussed in this subsection.
Chain Isomerism
It is also known as skeletal isomerism.
The components of these isomers display differently branched structures.
Commonly, chain isomers differ in the branching of carbon
Position Isomerism
The positions of the functional groups or substituent atoms are different in position isomers.
Typically, this isomerism involves the attachment of the functional groups to different carbon atoms in the carbon chain.
Functional Isomerism
It is also known as functional group isomerism.
As the name suggests, it refers to the compounds that have the same chemical formula but different functional groups attached to them.
Metamerism
This type of isomerism arises due to the presence of different alkyl chains on each side of the functional group.
It is a rare type of isomerism and is generally limited to molecules that contain a divalent atom (such as sulfur or oxygen), surrounded by alkyl groups.
Stereoisomerism
This type of isomerism arises in compounds having the same chemical formula but different orientations of the atoms belonging to the molecule in three-dimensional space. The compounds that exhibit stereoisomerism are often referred to as stereoisomers. This phenomenon can be further categorized into two subtypes. Both these subtypes are briefly described in this subsection.
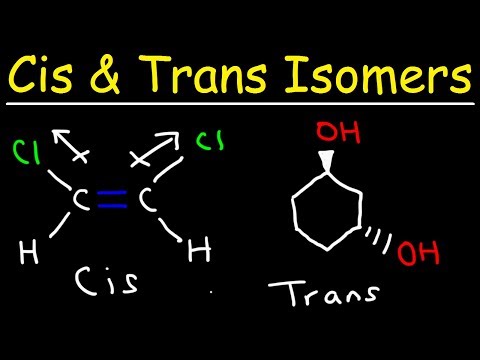
Geometric Isomerism
It is popularly known as cis-trans isomerism.
These isomers have different spatial arrangements of atoms in three-dimensional space
Optical Isomerism
Compounds that exhibit optical isomerism feature similar bonds but different spatial arrangements of atoms forming non-superimposable mirror images.
These optical isomers are also known as enantiomers.
Enantiomers differ from each other in their optical activities.
#Isomerism
#Isomers
#TypesofIsomerism
#MolecularFormula
#StructuralFormula
#Tautomers
#Structural
#Stereo
#Chain
#Positional
#Functional
#Metamerism
#Geometrical
#Confirmational
Different forms of the same molecule are known as structural isomers; they have the same molecular formula but are different 'shapes'.
Isomerism is the phenomenon in which more than one compounds have the same chemical formula but different chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formulae but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers.
There are two primary types of isomerism, which can be further categorized into different subtypes. These primary types are Structural Isomerism and Stereoisomerism.
Structural Isomerism
Structural isomerism is commonly referred to as constitutional isomerism. The functional groups and the atoms in the molecules of these isomers are linked in different ways. Different structural isomers are assigned different IUPAC names since they may or may not contain the same functional group. The different types of structural isomerism are discussed in this subsection.
Chain Isomerism
It is also known as skeletal isomerism.
The components of these isomers display differently branched structures.
Commonly, chain isomers differ in the branching of carbon
Position Isomerism
The positions of the functional groups or substituent atoms are different in position isomers.
Typically, this isomerism involves the attachment of the functional groups to different carbon atoms in the carbon chain.
Functional Isomerism
It is also known as functional group isomerism.
As the name suggests, it refers to the compounds that have the same chemical formula but different functional groups attached to them.
Metamerism
This type of isomerism arises due to the presence of different alkyl chains on each side of the functional group.
It is a rare type of isomerism and is generally limited to molecules that contain a divalent atom (such as sulfur or oxygen), surrounded by alkyl groups.
Stereoisomerism
This type of isomerism arises in compounds having the same chemical formula but different orientations of the atoms belonging to the molecule in three-dimensional space. The compounds that exhibit stereoisomerism are often referred to as stereoisomers. This phenomenon can be further categorized into two subtypes. Both these subtypes are briefly described in this subsection.
Geometric Isomerism
It is popularly known as cis-trans isomerism.
These isomers have different spatial arrangements of atoms in three-dimensional space
Optical Isomerism
Compounds that exhibit optical isomerism feature similar bonds but different spatial arrangements of atoms forming non-superimposable mirror images.
These optical isomers are also known as enantiomers.
Enantiomers differ from each other in their optical activities.
#Isomerism
#Isomers
#TypesofIsomerism
#MolecularFormula
#StructuralFormula
#Tautomers
#Structural
#Stereo
#Chain
#Positional
#Functional
#Metamerism
#Geometrical
#Confirmational
Комментарии
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:59:53
0:59:53
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:11:50
0:11:50
 0:15:34
0:15:34
 0:16:41
0:16:41
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 0:24:18
0:24:18
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:10:37
0:10:37
 0:13:10
0:13:10
 0:09:28
0:09:28
 0:47:13
0:47:13
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:12:54
0:12:54
 0:18:26
0:18:26
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:36:02
0:36:02
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:05:15
0:05:15
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:13:35
0:13:35