filmov
tv
Cell the Unit of Life | Cell Theory

Показать описание
Cell the Unit of Life : Cell Theory
Cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that describes the basic unit of life as the cell. It outlines the principles that form the foundation of modern cell biology. The cell theory has three main components:
1. All living organisms are composed of cells: Every living organism, from simple unicellular organisms to complex multicellular ones, is made up of one or more cells. Cells are the building blocks of life and carry out all the necessary functions for an organism's survival and growth.
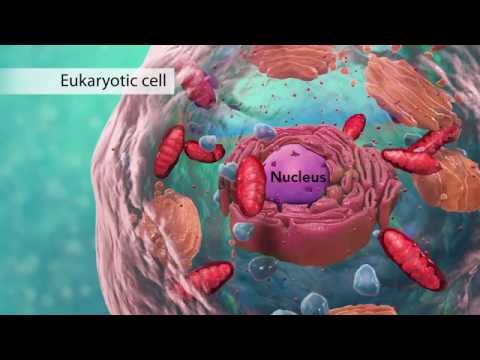
2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in living organisms: Cells are the smallest entities that exhibit the characteristics of life. They contain all the necessary structures and organelles to carry out essential processes such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells: Cells do not spontaneously generate but are produced from the division of pre-existing cells. This concept was popularized by the work of scientists like Rudolf Virchow, who stated, "Omnis cellula e cellula" (every cell originates from another existing cell).
The development of the cell theory is credited to several scientists who made significant contributions over time. Prominent figures include Robert Hooke, who observed and named cells in cork slices in the 17th century, and Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, who proposed the idea that all plants and animals are composed of cells in the 19th century.
The cell theory laid the groundwork for understanding the essential properties of living organisms and has played a crucial role in advancing biology, medicine, and other related fields. It continues to be a fundamental principle in modern biological research.
At Manocha Academy, learning Science and Math is Easy! The school coursework is explained with simple examples that you experience every day! Yes, Science & Math is all around you! Let's learn every day from everyday life!
Cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that describes the basic unit of life as the cell. It outlines the principles that form the foundation of modern cell biology. The cell theory has three main components:
1. All living organisms are composed of cells: Every living organism, from simple unicellular organisms to complex multicellular ones, is made up of one or more cells. Cells are the building blocks of life and carry out all the necessary functions for an organism's survival and growth.
2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in living organisms: Cells are the smallest entities that exhibit the characteristics of life. They contain all the necessary structures and organelles to carry out essential processes such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells: Cells do not spontaneously generate but are produced from the division of pre-existing cells. This concept was popularized by the work of scientists like Rudolf Virchow, who stated, "Omnis cellula e cellula" (every cell originates from another existing cell).
The development of the cell theory is credited to several scientists who made significant contributions over time. Prominent figures include Robert Hooke, who observed and named cells in cork slices in the 17th century, and Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, who proposed the idea that all plants and animals are composed of cells in the 19th century.
The cell theory laid the groundwork for understanding the essential properties of living organisms and has played a crucial role in advancing biology, medicine, and other related fields. It continues to be a fundamental principle in modern biological research.
At Manocha Academy, learning Science and Math is Easy! The school coursework is explained with simple examples that you experience every day! Yes, Science & Math is all around you! Let's learn every day from everyday life!
Комментарии
 0:07:22
0:07:22
 1:54:03
1:54:03
 0:26:37
0:26:37
 3:54:46
3:54:46
 0:53:04
0:53:04
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 1:24:22
1:24:22
 0:16:07
0:16:07
 1:04:35
1:04:35
 0:48:51
0:48:51
 0:09:27
0:09:27
 1:30:59
1:30:59
 0:53:23
0:53:23
 0:33:35
0:33:35
 0:40:35
0:40:35
 1:13:02
1:13:02
 5:30:34
5:30:34
 0:30:42
0:30:42
 1:21:41
1:21:41
 1:48:21
1:48:21
 0:29:47
0:29:47
 5:46:47
5:46:47
 3:08:31
3:08:31
 0:00:48
0:00:48