filmov
tv
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS - NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, MONOCYTE, LYMPHOCYTE

Показать описание
@lovemedics
WHITE BLOOD CELLS (WBC)
CONTENT
Introduction
Classification
Granular leucocytes
Agranular leucocytes
overview
INTRODUCTION
White blood cells are defined as white or colorless blood cells (corpuscle)
WBC/ Leucocytes
Leucocytes are the units of the body’s resistance to infection, disease
They are capable of amoeboid movement
FUNCTION
To protect the body against microorganisms causing disease.
LEUCOCYTES
They are formed in the
bone marrow from myeloid cells &
some being formed in the
lymph nodes from lymphoid cells
CLASSIFICATION
Two main groups
Granular
Agranular
Granular:
Neutrophils
Basophils
Eosinophils
Agranular:
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
GRANULAR LEUCOCYTES
NEUTROPHILS
Makeup 60 – 70 % of all white blood cells
The common type of WBC
Diameter: 10 – 12 micrometers
The nucleus contains 2- 5 lobes (multilobe) connected by a thin strands of chromatin
The cytoplasm has very fine, pale lilac granules
NEUTROPHILS FUNCTION
The first line of defense against infection.
Its function as a phagocyte (Ingestion of foreign bodies)
Destroy bacteria with lysozyme, defensins & strong oxidants such as superoxide anions hydrogen peroxide & hydrochloride anion
BASOPHILS
Makeup 0.5 – 1% of all white blood cells
Diameter: 8 - 10 micrometers
The nucleus contains 2 lobes
(Irregular or ‘s-shaped)
The cytoplasm contains coarse granules which take up the basophilic stain
It remains in the blood for a short duration & later migrates to the tissues.
BASOPHILS FUNCTION
They are responsible for fighting bacterial & fungal infection
Basophils Liberate
Heparin – Anticoagulant substance
Histamine – Allergic reaction
Serotonin – Inflammatory process
EOSINOPHILS
Made up 2-4% of all white blood cells
Diameter: 10 – 12 micrometers
Its nucleus has 2 or 3 lobes /spectacle-shaped
The cytoplasm contains coarse granules, oval or round in shape, which take up acid stain & appear orange-colored with eosin.
EOSINOPHILS FUNCTION
Eosinophils are antiallergic in function
Phagocytize Ag – Ab complexes
Mediate the inflammation
The eosinophil count increases during parasitic infection
They migrate towards the larvae of the parasite, bind to it,
Destroy them by releasing hydrolytic enzymes, major proteins & forming superoxides
AGRANULAR LEUCOCYTES
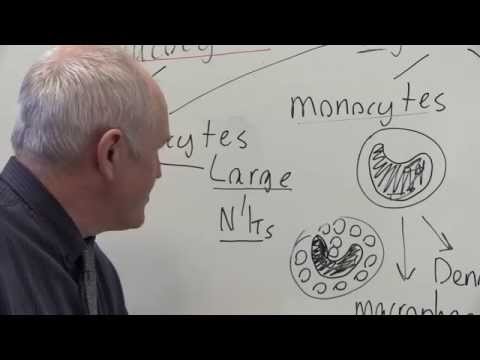
MONOCYTES
Made up 3- 8 % of all white blood cells
Very larger cells
Diameter: 12 – 20 micrometers
The nucleus is kidney-shaped or horseshoe-shaped
The cytoplasm is pale blue on staining & do not contain granules
MONOCYTES
The life span of monocyte in the blood is around 10 – 20 hours & later they migrate to the tissues
In the tissues, they become large in size to form tissue macrophages. They remain in tissues for months to years.
MONOCYTES FUNCTION
Monocytes form the second line of defense
They are also Phagocytic
They are immature cells in the blood & do not have the full ability to fight against infection.
But, once they enter the tissue, they are converted to tissue macrophages (lung, liver, spleen tissue) which enlarge to attain a size of about 80 micrometers.
A single macrophage can digest around 100 bacteria. After digestion, the digested particles are extruded.
Help to remove the dead cells.
LYMPHOCYTES
Makeup 20 – 25% of all white blood cells
The nucleus is rounded or slightly indented
Cytoplasm forms a rim around the nucleus that looks sky blue
Each lymphocyte bears receptors that bind to a specific antigen
LYMPHOCYTES
Morphologically, they are 2 types.
Small lymphocytes: Diameter: 6- 9 micrometers
They have a large nucleus
Large lymphocytes: Diameter: 1 - 14 micrometers
More cytoplasm is visible
Lymphocytes
Functionally, they are of two types.
T cells – cell-mediated immunity
B cells - Antibody-mediated immunity
LYMPHOCYTES FUNCTION
Lymphocytes are involved in immunity
T – Lymphocytes are concerned with
cell-mediated immunity
T cells attack invading viruses, cancer cells & transplanted tissue cells
They are 5 subtypes.
Cytotoxic T cells
Helper T cells
Memory T cells
Suppressor T cells
Natural killer cells
LYMPHOCYTES FUNCTION
B – Lymphocytes get transformed into plasma
they form immunoglobulin
& are responsible for humoral immunity
LEUCOCYTES - FUNCTION
Antibody formation
Fibroblast formation
Phagocyte - Neutrophil, Monocyte
Kill the tumor cells - T Lymphocyte
Prevent intravascular clotting - Basophil
Allergic condition - Eosinophil
#lovemedics #anatomy #physiology #wbcs
WHITE BLOOD CELLS (WBC)
CONTENT
Introduction
Classification
Granular leucocytes
Agranular leucocytes
overview
INTRODUCTION
White blood cells are defined as white or colorless blood cells (corpuscle)
WBC/ Leucocytes
Leucocytes are the units of the body’s resistance to infection, disease
They are capable of amoeboid movement
FUNCTION
To protect the body against microorganisms causing disease.
LEUCOCYTES
They are formed in the
bone marrow from myeloid cells &
some being formed in the
lymph nodes from lymphoid cells
CLASSIFICATION
Two main groups
Granular
Agranular
Granular:
Neutrophils
Basophils
Eosinophils
Agranular:
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
GRANULAR LEUCOCYTES
NEUTROPHILS
Makeup 60 – 70 % of all white blood cells
The common type of WBC
Diameter: 10 – 12 micrometers
The nucleus contains 2- 5 lobes (multilobe) connected by a thin strands of chromatin
The cytoplasm has very fine, pale lilac granules
NEUTROPHILS FUNCTION
The first line of defense against infection.
Its function as a phagocyte (Ingestion of foreign bodies)
Destroy bacteria with lysozyme, defensins & strong oxidants such as superoxide anions hydrogen peroxide & hydrochloride anion
BASOPHILS
Makeup 0.5 – 1% of all white blood cells
Diameter: 8 - 10 micrometers
The nucleus contains 2 lobes
(Irregular or ‘s-shaped)
The cytoplasm contains coarse granules which take up the basophilic stain
It remains in the blood for a short duration & later migrates to the tissues.
BASOPHILS FUNCTION
They are responsible for fighting bacterial & fungal infection
Basophils Liberate
Heparin – Anticoagulant substance
Histamine – Allergic reaction
Serotonin – Inflammatory process
EOSINOPHILS
Made up 2-4% of all white blood cells
Diameter: 10 – 12 micrometers
Its nucleus has 2 or 3 lobes /spectacle-shaped
The cytoplasm contains coarse granules, oval or round in shape, which take up acid stain & appear orange-colored with eosin.
EOSINOPHILS FUNCTION
Eosinophils are antiallergic in function
Phagocytize Ag – Ab complexes
Mediate the inflammation
The eosinophil count increases during parasitic infection
They migrate towards the larvae of the parasite, bind to it,
Destroy them by releasing hydrolytic enzymes, major proteins & forming superoxides
AGRANULAR LEUCOCYTES
MONOCYTES
Made up 3- 8 % of all white blood cells
Very larger cells
Diameter: 12 – 20 micrometers
The nucleus is kidney-shaped or horseshoe-shaped
The cytoplasm is pale blue on staining & do not contain granules
MONOCYTES
The life span of monocyte in the blood is around 10 – 20 hours & later they migrate to the tissues
In the tissues, they become large in size to form tissue macrophages. They remain in tissues for months to years.
MONOCYTES FUNCTION
Monocytes form the second line of defense
They are also Phagocytic
They are immature cells in the blood & do not have the full ability to fight against infection.
But, once they enter the tissue, they are converted to tissue macrophages (lung, liver, spleen tissue) which enlarge to attain a size of about 80 micrometers.
A single macrophage can digest around 100 bacteria. After digestion, the digested particles are extruded.
Help to remove the dead cells.
LYMPHOCYTES
Makeup 20 – 25% of all white blood cells
The nucleus is rounded or slightly indented
Cytoplasm forms a rim around the nucleus that looks sky blue
Each lymphocyte bears receptors that bind to a specific antigen
LYMPHOCYTES
Morphologically, they are 2 types.
Small lymphocytes: Diameter: 6- 9 micrometers
They have a large nucleus
Large lymphocytes: Diameter: 1 - 14 micrometers
More cytoplasm is visible
Lymphocytes
Functionally, they are of two types.
T cells – cell-mediated immunity
B cells - Antibody-mediated immunity
LYMPHOCYTES FUNCTION
Lymphocytes are involved in immunity
T – Lymphocytes are concerned with
cell-mediated immunity
T cells attack invading viruses, cancer cells & transplanted tissue cells
They are 5 subtypes.
Cytotoxic T cells
Helper T cells
Memory T cells
Suppressor T cells
Natural killer cells
LYMPHOCYTES FUNCTION
B – Lymphocytes get transformed into plasma
they form immunoglobulin
& are responsible for humoral immunity
LEUCOCYTES - FUNCTION
Antibody formation
Fibroblast formation
Phagocyte - Neutrophil, Monocyte
Kill the tumor cells - T Lymphocyte
Prevent intravascular clotting - Basophil
Allergic condition - Eosinophil
#lovemedics #anatomy #physiology #wbcs
 0:22:16
0:22:16
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:21:33
0:21:33
 0:28:29
0:28:29
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:08:16
0:08:16
 0:16:30
0:16:30
 0:06:06
0:06:06
 0:10:14
0:10:14
 0:09:47
0:09:47
 0:31:39
0:31:39
 0:14:08
0:14:08
 0:12:52
0:12:52
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:15:01
0:15:01
 0:37:14
0:37:14
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:17:19
0:17:19
 0:17:33
0:17:33
 0:10:44
0:10:44
 0:18:46
0:18:46