filmov
tv
FOR Loop in Python (Syntax, Break, Continue, Else, Nested Loop, Range, Index) - Python for Beginners

Показать описание
🎓 Welcome back to Digital Academy, the Complete Python Development Tutorial for Beginners, which will help you repeat a block of code for a fixed number of times, using FOR Loops in Python - and alter its behaviour with CONTINUE, BREAK and ELSE keywords in Python!
▬▬▬▬ 📖 Content ▬▬▬▬
🖥️ Loops in Python are an efficient method for optimising your code, and executing multiple statements. If the same block of code has to be executed, multiple times, over and over: you can put it into a Loop, to perform multiple iterations. Consequently: it saves a lot of effort, and reduces complexity of your Python code, as well.
Basically, there are two types of Loops, in programming languages:
○ Indefinite iteration: In which the code block executes, until some condition is met. This iteration is performed using WHILE Loops, and will be discussed in the very next upcoming video.
○ Definite iteration: In which the number of repetitions is specified, explicitly and in advance. This kind of iteration is performed using FOR Loops, and will be discussed in this video.
FOR Loops in Python are traditionally used when you have a block of code which you want to repeat, a fixed number of times. It iterates over the members of a sequence (strings, dictionaries, lists, tuples and sets - or any other iterable objects), then executes the same block of code, each time - and in order.
You can also alter the behaviour of the current iteration inside the Loop, using BREAK and CONTINUE statements .Then execute a block of code when the Loop terminates naturally, or reaches the last item of a sequence.
🎯 In this video, you will discover multiple way to control the execution flow of your program, using FOR Loops in Python. Then, you will learn how you can alter the execution of an iteration, with: BREAK, CONTINUE and ELSE statements in Python.
Finally, you will discover the function range() in Python: to generate a sequence of numbers and execute a block of code, a fixed number of times. It can be combined with the len() function, to iterate through a sequence using indexing. This way, you can get the index of the current item, in the list (enumerate)
Let's play this video, stick around and watch until the end! 👍🏻
- Digital Academy™ 🎓
▬▬▬▬ 🎬 Watch NEXT ▬▬▬▬
▬▬▬▬ 🔗 Links ▬▬▬▬
▬▬▬▬ ⏱ Timestamps ▬▬▬▬
00:00 | Intro
00:09 | Introduction
01:05 | Python Loops
01:58 | Python FOR Loops
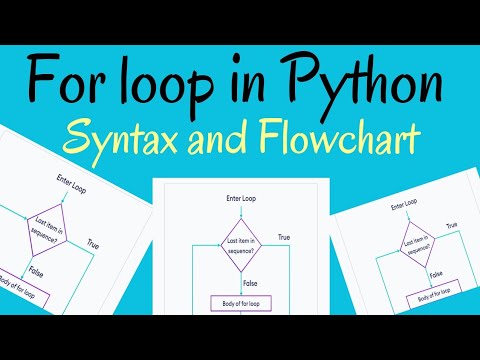
02:40 | Python FOR - Syntax
03:44 | Python FOR - Examples
05:20 | Python FOR - BREAK in Python
07:35 | Python FOR - CONTINUE in Python
08:51 | Python FOR - ELSE in Python
10:15 | Python FOR - Nested Loops in Python
10:44 | Python FOR - range() function in Python
13:04 | Python FOR - enumerate() function in Python
13:50 | Conclusion
14:23 | Subscribe, Like, Comment & Share
#Python #Tutorial #Beginners #For #Loops
▬▬▬▬ ⭐ FOLLOW US ▬▬▬▬
▬▬▬▬ ⚡ SUPPORT US ▬▬▬▬
▬▬▬▬ 📖 Content ▬▬▬▬
🖥️ Loops in Python are an efficient method for optimising your code, and executing multiple statements. If the same block of code has to be executed, multiple times, over and over: you can put it into a Loop, to perform multiple iterations. Consequently: it saves a lot of effort, and reduces complexity of your Python code, as well.
Basically, there are two types of Loops, in programming languages:
○ Indefinite iteration: In which the code block executes, until some condition is met. This iteration is performed using WHILE Loops, and will be discussed in the very next upcoming video.
○ Definite iteration: In which the number of repetitions is specified, explicitly and in advance. This kind of iteration is performed using FOR Loops, and will be discussed in this video.
FOR Loops in Python are traditionally used when you have a block of code which you want to repeat, a fixed number of times. It iterates over the members of a sequence (strings, dictionaries, lists, tuples and sets - or any other iterable objects), then executes the same block of code, each time - and in order.
You can also alter the behaviour of the current iteration inside the Loop, using BREAK and CONTINUE statements .Then execute a block of code when the Loop terminates naturally, or reaches the last item of a sequence.
🎯 In this video, you will discover multiple way to control the execution flow of your program, using FOR Loops in Python. Then, you will learn how you can alter the execution of an iteration, with: BREAK, CONTINUE and ELSE statements in Python.
Finally, you will discover the function range() in Python: to generate a sequence of numbers and execute a block of code, a fixed number of times. It can be combined with the len() function, to iterate through a sequence using indexing. This way, you can get the index of the current item, in the list (enumerate)
Let's play this video, stick around and watch until the end! 👍🏻
- Digital Academy™ 🎓
▬▬▬▬ 🎬 Watch NEXT ▬▬▬▬
▬▬▬▬ 🔗 Links ▬▬▬▬
▬▬▬▬ ⏱ Timestamps ▬▬▬▬
00:00 | Intro
00:09 | Introduction
01:05 | Python Loops
01:58 | Python FOR Loops
02:40 | Python FOR - Syntax
03:44 | Python FOR - Examples
05:20 | Python FOR - BREAK in Python
07:35 | Python FOR - CONTINUE in Python
08:51 | Python FOR - ELSE in Python
10:15 | Python FOR - Nested Loops in Python
10:44 | Python FOR - range() function in Python
13:04 | Python FOR - enumerate() function in Python
13:50 | Conclusion
14:23 | Subscribe, Like, Comment & Share
#Python #Tutorial #Beginners #For #Loops
▬▬▬▬ ⭐ FOLLOW US ▬▬▬▬
▬▬▬▬ ⚡ SUPPORT US ▬▬▬▬
Комментарии
 0:05:06
0:05:06
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:07:27
0:07:27
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:04:30
0:04:30
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:08:14
0:08:14
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:53:34
0:53:34
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:24:59
0:24:59
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:15:07
0:15:07
 0:12:24
0:12:24
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:13:01
0:13:01
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:01:01
0:01:01