filmov
tv
Eye Anatomy and Physiology Simplified (in Hindi)

Показать описание
Eye Anatomy and Physiology Simplified (in Hindi)
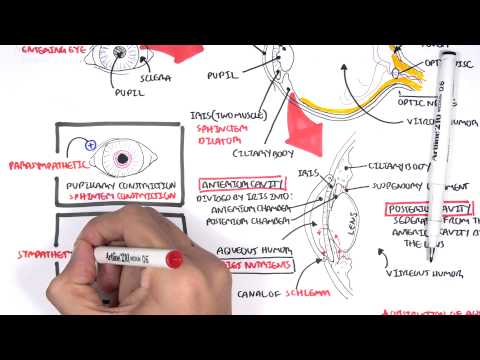
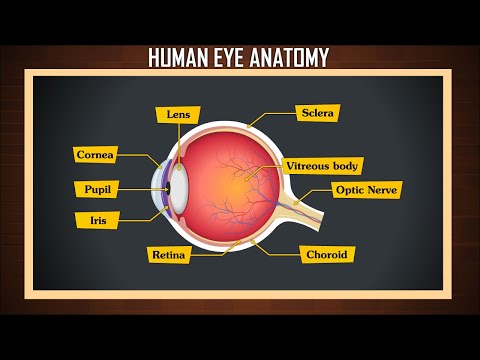
Choroid -
Layer containing blood vessels that lines the back of the eye and is located between the retina (the inner light-sensitive layer) and the sclera (the outer white eye wall).
Ciliary Body-
Structure containing muscle and is located behind the iris, which focuses the lens.
Cornea-
The clear front window of the eye which transmits and focuses (i.e., sharpness or clarity) light into the eye. Corrective laser surgery reshapes the cornea, changing the focus.
Fovea-
The center of the macula which provides the sharp vision.
Iris-
The colored part of the eye which helps regulate the amount of light entering the eye. When there is bright light, the iris closes the pupil to let in less light. And when there is low light, the iris opens up the pupil to let in more light.
Lens -
Focuses light rays onto the retina. The lens is transparent, and can be replaced if necessary. Our lens deteriorates as we age, resulting in the need for reading glasses. Intraocular lenses are used to replace lenses clouded by cataracts.
Macula-
The area in the retina that contains special light-sensitive cells. In the macula these light-sensitive cells allow us to see fine details clearly in the center of our visual field. The deterioration of the macula is a common condition as we get older (age related macular degeneration or ARMD).
Optic Nerve-
A bundle of more than a million nerve fibers carrying visual messages from the retina to the brain. (In order to see, we must have light and our eyes must be connected to the brain.) Your brain actually controls what you see, since it combines images. The retina sees images upside down but the brain turns images right side up. This reversal of the images that we see is much like a mirror in a camera. Glaucoma is one of the most common eye conditions related to optic nerve damage.
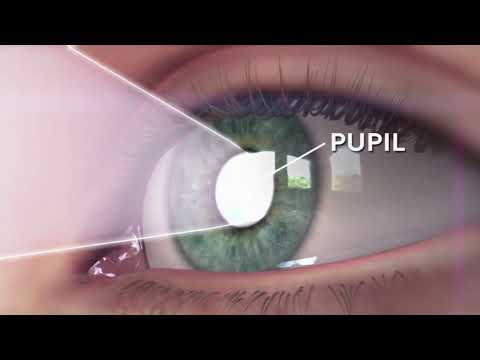
Pupil-
The dark center opening in the middle of the iris. The pupil changes size to adjust for the amount of light available (smaller for bright light and larger for low light). This opening and closing of light into the eye is much like the aperture in most 35 mm cameras which lets in more or less light depending upon the conditions.
Retina-
The nerve layer lining the back of the eye. The retina senses light and creates electrical impulses that are sent through the optic nerve to the brain.
Sclera-
The white outer coat of the eye, surrounding the iris.
Vitreous Humor-
The, clear, gelatinous substance filling the central cavity of the eye.
(Credit: Michigan Medicine)
Choroid -
Layer containing blood vessels that lines the back of the eye and is located between the retina (the inner light-sensitive layer) and the sclera (the outer white eye wall).
Ciliary Body-
Structure containing muscle and is located behind the iris, which focuses the lens.
Cornea-
The clear front window of the eye which transmits and focuses (i.e., sharpness or clarity) light into the eye. Corrective laser surgery reshapes the cornea, changing the focus.
Fovea-
The center of the macula which provides the sharp vision.
Iris-
The colored part of the eye which helps regulate the amount of light entering the eye. When there is bright light, the iris closes the pupil to let in less light. And when there is low light, the iris opens up the pupil to let in more light.
Lens -
Focuses light rays onto the retina. The lens is transparent, and can be replaced if necessary. Our lens deteriorates as we age, resulting in the need for reading glasses. Intraocular lenses are used to replace lenses clouded by cataracts.
Macula-
The area in the retina that contains special light-sensitive cells. In the macula these light-sensitive cells allow us to see fine details clearly in the center of our visual field. The deterioration of the macula is a common condition as we get older (age related macular degeneration or ARMD).
Optic Nerve-
A bundle of more than a million nerve fibers carrying visual messages from the retina to the brain. (In order to see, we must have light and our eyes must be connected to the brain.) Your brain actually controls what you see, since it combines images. The retina sees images upside down but the brain turns images right side up. This reversal of the images that we see is much like a mirror in a camera. Glaucoma is one of the most common eye conditions related to optic nerve damage.
Pupil-
The dark center opening in the middle of the iris. The pupil changes size to adjust for the amount of light available (smaller for bright light and larger for low light). This opening and closing of light into the eye is much like the aperture in most 35 mm cameras which lets in more or less light depending upon the conditions.
Retina-
The nerve layer lining the back of the eye. The retina senses light and creates electrical impulses that are sent through the optic nerve to the brain.
Sclera-
The white outer coat of the eye, surrounding the iris.
Vitreous Humor-
The, clear, gelatinous substance filling the central cavity of the eye.
(Credit: Michigan Medicine)
Комментарии
 0:02:49
0:02:49
 0:17:05
0:17:05
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:07:20
0:07:20
 0:09:55
0:09:55
 0:02:21
0:02:21
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:45:46
0:45:46
 0:05:09
0:05:09
 0:09:21
0:09:21
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:09:52
0:09:52
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:10:14
0:10:14
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:10:22
0:10:22
 0:02:57
0:02:57