filmov
tv
Oracle 12c Database New Features - Pluggable Database - Video 1
Показать описание
Oracle 12c Database New Features - Pluggable Database - Video 1
1. Pluggable Database
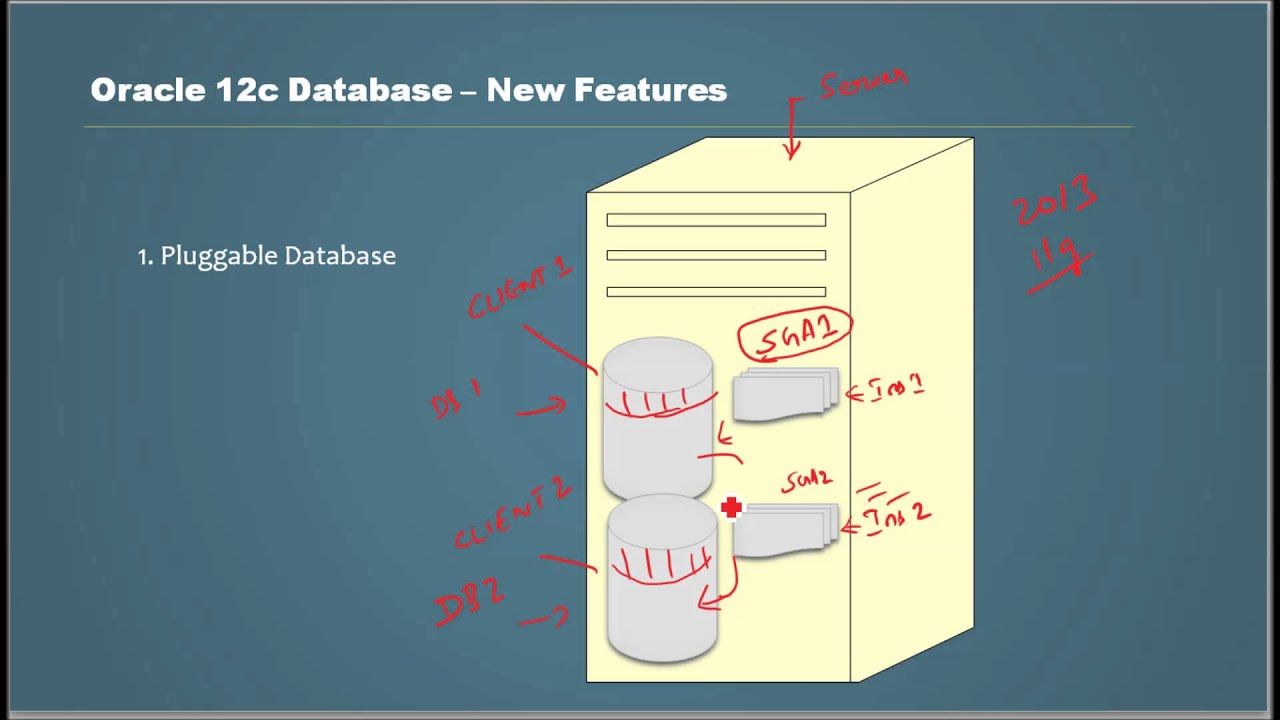
* Oracle 12c introduces a new feature called 'Pluggable Database'. Here Oracle Metadata and user data are totally separated into two sections. One is Container DB (or CDB) which will hold Oracle Metadata. The other is Pluggable DB (or PDB) which will hold user data.
How does a Pluggable Database work?
In the regular database, Oracle's metadata and user's application data are integrated. For beginners, Oracle Metadata is the data that is present when you install a new Oracle Database (without any sample schemas). Even though it can be called as an empty database, it still has data provided by Oracle. This data is needed by the database to function. For example, the objects owned by SYS, SYSTEM are mostly metadata.
Then user data is entered into that database. They will go under multiple user schemas. Now the database is being used by the users.
Now a situation arises so that we need to create another database on the same server. Why? Let us say that you need to provide data to two clients. And you don't want one client to other's data. And your data is contained in an extensive set of application schemas.
In this case, making a copy of those applications schemas into a different set of names and making them reside in the same database is very difficult.
So, you provide two separate databases. This also ensures that there is no security violation.
So, we install another new database, which comes with Oracle Metadata. Then we load the user data. In this method, which is currently being used (Year 2013), there will be a need for more memory for both the database instances. There will be two SGAs, two sets of smon, pmon and other background processes running.
Then if we need to copy one database to another, we need to rely on extensive procedures which includes exporting the data from the source database first, then removing the data at the target and then finally loading the data in there. After that, we need to take care of the user security and object privileges etc.
So, if you want to provide data for multiple tenants, that is multiple clients, then with the current set of features (till Oracle 11g), we have to create multiple databases. That is, one database for one client. In otherwords, there is no multi-tenancy.
Multi-Tenancy is becoming an important requirement in cloud infrastructure, these days. You would like to have the ability of providing data to multiple clients from the same database system with full confidence in security.
This can be achieved in Pluggable Database.
In a Pluggable Database, Oracle basically separates its metadata entirely from the user data. Metadata is stored in a section called Container DB. Then the user data are stored in Pluggable DBs. It also stores user metadata in the Pluggable DB.
By the way, what is user metadata? For example, earlier, the list of user accounts that exist in a database is tightly inegrated with Oracle Metadata. Now, with the separation of Container DB and Pluggable DB, the user accounts must exist in the Pluggable DB. So, the Pluggable DB not only contains user data, but also some user metadata.
So, what are the benefits?
* Multi-Tenancy - We can bring in two Pluggable DBs under one Container DB. Both will be totally segregated, but yet controlled by one instance. This is an important feature for SaaS (Software as a Service) platforms, Cloud, On-Demand and Vendor Managed Application solutions.
* Easy cloning/copying. Now the cloning and copying the databases across servers would be much easier. Just clone a Pluggable DB and plug-it-in in a different server.
* Very easy upgrades and patching.
1. Pluggable Database
* Oracle 12c introduces a new feature called 'Pluggable Database'. Here Oracle Metadata and user data are totally separated into two sections. One is Container DB (or CDB) which will hold Oracle Metadata. The other is Pluggable DB (or PDB) which will hold user data.
How does a Pluggable Database work?
In the regular database, Oracle's metadata and user's application data are integrated. For beginners, Oracle Metadata is the data that is present when you install a new Oracle Database (without any sample schemas). Even though it can be called as an empty database, it still has data provided by Oracle. This data is needed by the database to function. For example, the objects owned by SYS, SYSTEM are mostly metadata.
Then user data is entered into that database. They will go under multiple user schemas. Now the database is being used by the users.
Now a situation arises so that we need to create another database on the same server. Why? Let us say that you need to provide data to two clients. And you don't want one client to other's data. And your data is contained in an extensive set of application schemas.
In this case, making a copy of those applications schemas into a different set of names and making them reside in the same database is very difficult.
So, you provide two separate databases. This also ensures that there is no security violation.
So, we install another new database, which comes with Oracle Metadata. Then we load the user data. In this method, which is currently being used (Year 2013), there will be a need for more memory for both the database instances. There will be two SGAs, two sets of smon, pmon and other background processes running.
Then if we need to copy one database to another, we need to rely on extensive procedures which includes exporting the data from the source database first, then removing the data at the target and then finally loading the data in there. After that, we need to take care of the user security and object privileges etc.
So, if you want to provide data for multiple tenants, that is multiple clients, then with the current set of features (till Oracle 11g), we have to create multiple databases. That is, one database for one client. In otherwords, there is no multi-tenancy.
Multi-Tenancy is becoming an important requirement in cloud infrastructure, these days. You would like to have the ability of providing data to multiple clients from the same database system with full confidence in security.
This can be achieved in Pluggable Database.
In a Pluggable Database, Oracle basically separates its metadata entirely from the user data. Metadata is stored in a section called Container DB. Then the user data are stored in Pluggable DBs. It also stores user metadata in the Pluggable DB.
By the way, what is user metadata? For example, earlier, the list of user accounts that exist in a database is tightly inegrated with Oracle Metadata. Now, with the separation of Container DB and Pluggable DB, the user accounts must exist in the Pluggable DB. So, the Pluggable DB not only contains user data, but also some user metadata.
So, what are the benefits?
* Multi-Tenancy - We can bring in two Pluggable DBs under one Container DB. Both will be totally segregated, but yet controlled by one instance. This is an important feature for SaaS (Software as a Service) platforms, Cloud, On-Demand and Vendor Managed Application solutions.
* Easy cloning/copying. Now the cloning and copying the databases across servers would be much easier. Just clone a Pluggable DB and plug-it-in in a different server.
* Very easy upgrades and patching.
Комментарии
 0:45:32
0:45:32
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:09:42
0:09:42
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:25:27
0:25:27
 0:14:13
0:14:13
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:56:13
0:56:13
 1:10:18
1:10:18
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:11:42
0:11:42
 0:29:22
0:29:22
 0:12:43
0:12:43
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 1:35:49
1:35:49
 0:03:54
0:03:54
 0:24:52
0:24:52
 0:27:05
0:27:05
 0:50:49
0:50:49
 0:14:09
0:14:09
 0:01:54
0:01:54
 0:28:03
0:28:03
 0:49:13
0:49:13