filmov
tv
REVERSE OSMOSIS OR RO SYSTEM FOR SEAWATER DESALINATION PLANT

Показать описание
REVERSE OSMOSIS OR REVERSE OSMOSIS SYSTEM
SWRO Plant Training series
LP flow rate set by discharge flow control valve (LP-PX inlet flow meter)
HP flow rate set by VFD –Booster pump ( with booster inlet flowmeter)
RO Plant Operation
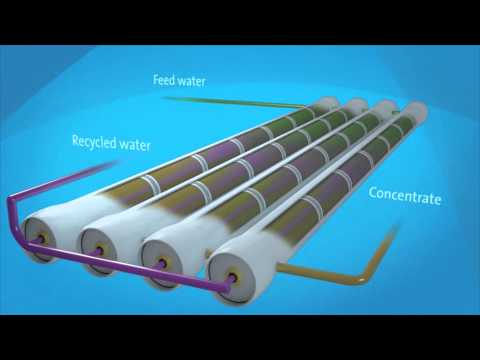
Each train consists of the following main components:
High pressure pump
b) Pressure exchangers
c) Booster pump
d) Pressure vessels and RO Elements (RO Module)
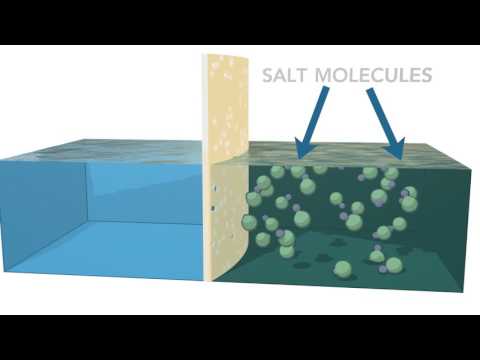
In the RO stage salt in the raw water is removed by means of a special membrane filters.
To make the separation process working, the osmotic pressure between brine (concentrate) and permeate (salt reduced water) has to be overcome by means of a high pressure feed pump
To make the system more energy efficient, the remaining high pressure of the brine is used to drive the PX (pressure exchanger), which is feeding additional raw water to the membranes.
Permeate flow rate set by high pressure pump and membranes with FCV and HP outlet flowmeter
LP control valve does not directly affect membrane pressure
System pressure determined by membrane condition, feed temperature and feed salinity
Supply pressure changes cause LP flow rate changes to avoid change supply pressure should be maintained at constant valve between 2.3 – 2.6 bar
PX™ LP out pressure must be maintained above minimum 1 bar to avoid cavitation
RO System Operation
The plant operation parameters have to be adjusted to changing requirements and conditions. RO plants are usually operated at constant flow and recovery. Changes in membrane flux are compensated by adjusting the feed pressure.
Decreasing temperature and increase in feed water salinity can be compensated by increasing the feed pressure. Once the maximum pressure is reached, a further decrease results in lower productivity.
Increasing temperature is compensated by lowering the feed pressure. This may lead to increase in permeate TDS.
Lower feed water salinity allows decreasing feed pressure
SWRO Plant Training series
LP flow rate set by discharge flow control valve (LP-PX inlet flow meter)
HP flow rate set by VFD –Booster pump ( with booster inlet flowmeter)
RO Plant Operation
Each train consists of the following main components:
High pressure pump
b) Pressure exchangers
c) Booster pump
d) Pressure vessels and RO Elements (RO Module)
In the RO stage salt in the raw water is removed by means of a special membrane filters.
To make the separation process working, the osmotic pressure between brine (concentrate) and permeate (salt reduced water) has to be overcome by means of a high pressure feed pump
To make the system more energy efficient, the remaining high pressure of the brine is used to drive the PX (pressure exchanger), which is feeding additional raw water to the membranes.
Permeate flow rate set by high pressure pump and membranes with FCV and HP outlet flowmeter
LP control valve does not directly affect membrane pressure
System pressure determined by membrane condition, feed temperature and feed salinity
Supply pressure changes cause LP flow rate changes to avoid change supply pressure should be maintained at constant valve between 2.3 – 2.6 bar
PX™ LP out pressure must be maintained above minimum 1 bar to avoid cavitation
RO System Operation
The plant operation parameters have to be adjusted to changing requirements and conditions. RO plants are usually operated at constant flow and recovery. Changes in membrane flux are compensated by adjusting the feed pressure.
Decreasing temperature and increase in feed water salinity can be compensated by increasing the feed pressure. Once the maximum pressure is reached, a further decrease results in lower productivity.
Increasing temperature is compensated by lowering the feed pressure. This may lead to increase in permeate TDS.
Lower feed water salinity allows decreasing feed pressure
 0:06:55
0:06:55
 0:01:06
0:01:06
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:11:48
0:11:48
 0:01:26
0:01:26
 0:08:25
0:08:25
 0:07:10
0:07:10
 0:11:34
0:11:34
 0:16:37
0:16:37
 0:22:29
0:22:29
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:11:12
0:11:12
 0:08:24
0:08:24
 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:10:37
0:10:37
 0:11:36
0:11:36
 0:12:34
0:12:34
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:08:43
0:08:43
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:33:38
0:33:38
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:11:55
0:11:55