filmov
tv
Python Class 17 - Python Built-in Functions

Показать описание
The Python interpreter has a number of functions and types built into it that are always available.
Python Built-in Functions, Types of Functions, User Defined Functions, Strings Functions, Math Functions, and Input & Output Functions.
Python Functions, What is Function?, Types of Python Functions, Create Python Functions, Calling a Python Function, and Functions Advantages.
1. What is Function?
2. Types of Functions in Python
3. Advantages of Functions
4. User-Defined Functions
5. Python Function with return a value
6. Python Function with returns nothing
7. Python Functions with Arguments
8. Python Function with default parameters
There are mainly two types of functions in Python.
1. User-defined functions – The user-defined functions are those defined by the user to perform the specific task.
2. Built-in functions – The built-in functions are those functions that are pre-defined in Python.
Python Complete Tutorial
Python Videos PlayList
Python Programming Syllabus
Python Programming Quiz
Python Interview Questions for Fresher
--------------------------------------------------
1. Introduction to Python Programming Language
2. Download and Install Python
Python Environment Setup (Using PyCharm IDE)
3. Python Language Syntax
4. Python Keywords and Identifiers
5. Comments in Python
6. Python Variables
7. Python Data Types
8. Python Operators
9. Python Conditional Statements
10. Python Loops
11. Python Branching Statements
12. Python Numbers
13. String Handling in Python
14. Python Data Structures - Lists
15. Python Data Structures - Sets
16. Python Data Structures - Tuples
17. Python Data Structures - Dictionaries
18. Python User Defined Functions
19. Python Built-in Functions
20. Python Modules
21. Python User Input
22. File Handling in Python
23. Python Date and Time
24. Python Exception Handling
25. Python Regular Expressions
26. Python Object Oriented Programming
27. Inheritance in Python
28. Polymorphism in Python
29. Abstraction in Python
--------------------------------------------------
Комментарии
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:09:17
0:09:17
 0:18:52
0:18:52
 0:13:42
0:13:42
 0:15:00
0:15:00
 0:15:24
0:15:24
 0:08:01
0:08:01
 0:11:47
0:11:47
 11:55:00
11:55:00
 0:10:32
0:10:32
 0:06:46
0:06:46
 0:09:50
0:09:50
 0:27:45
0:27:45
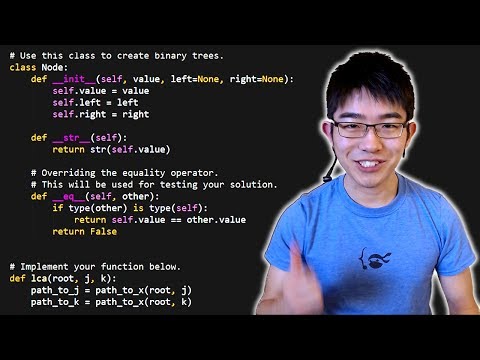 0:11:36
0:11:36
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:10:01
0:10:01
 0:11:41
0:11:41
 0:11:01
0:11:01
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:25:39
0:25:39
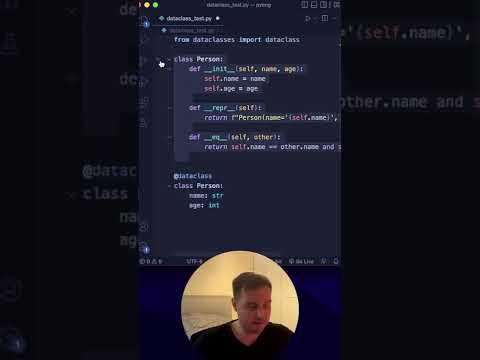 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:13:01
0:13:01
 0:15:51
0:15:51
 0:10:17
0:10:17