filmov
tv
Spring Boot Kafka Tutorial | Mastering Kafka with Spring Boot | Apache Kafka Crash Course
Показать описание
Welcome to our comprehensive guide to using Apache Kafka with Spring Boot! In this video, we delve into the fundamental concepts and advanced techniques that will empower you to harness the full potential of Kafka in your applications.
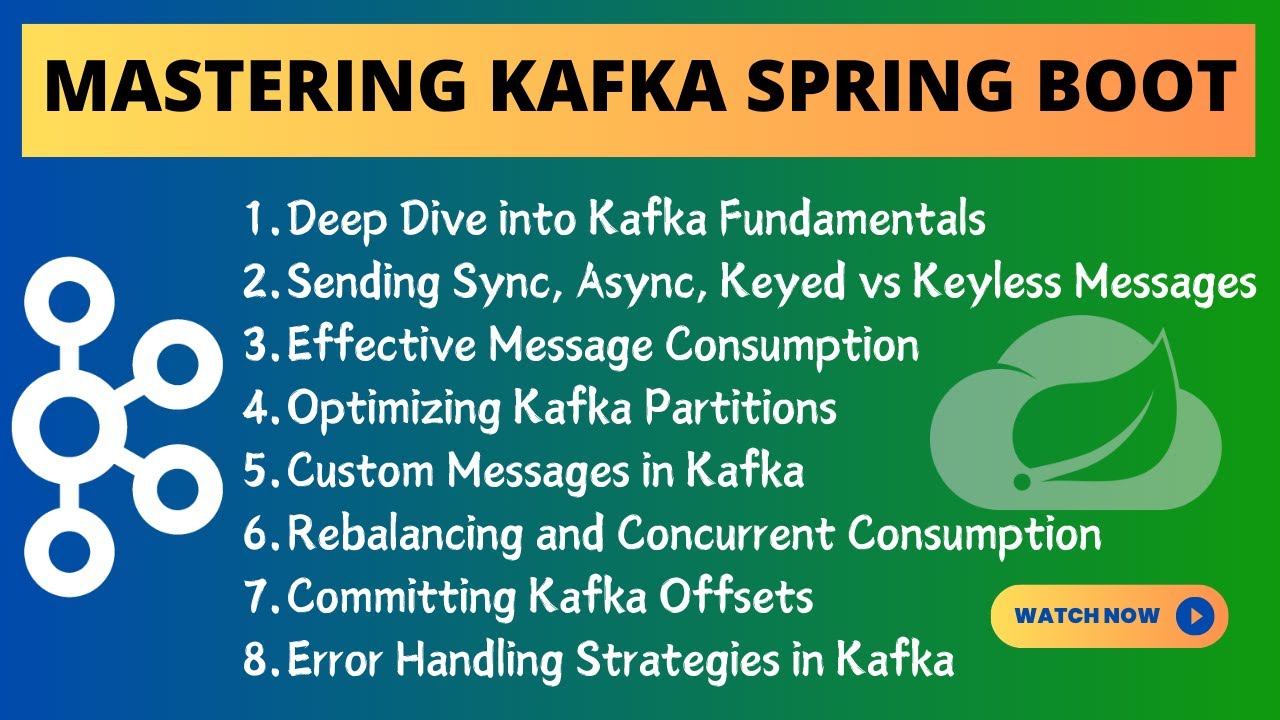
We start with the basics, covering what Kafka is and its key components such as producers, consumers, topics, and partitions. You'll learn about the flow of data within Kafka and explore real-world use cases where Kafka shines.
Next, we dive into practical demonstrations. Discover how to create Kafka producers efficiently and send messages both synchronously and asynchronously. Learn the nuances of sending messages with and without keys, and explore strategies for efficient message routing and consumption.
We then explore advanced topics including custom message production and consumption, handling consumer partition rebalancing with multiple consumers, and optimizing offset commitments for reliability.
Throughout the video, we emphasize best practices for error handling and discuss considerations for deploying Kafka applications outside of cloud environments or Kubernetes.
Whether you're new to Kafka or looking to deepen your understanding, this video provides actionable insights and practical examples that will accelerate your journey towards mastering Kafka with Spring Boot.
Don't forget to like, comment, and subscribe for more tutorials on Spring Boot, Kafka, and other cutting-edge technologies!
START THE KAFKA ENVIRONMENT:
NOTE: Your local environment must have Java 8+ installed.
Apache Kafka can be started using ZooKeeper or KRaft. To get started with either configuration follow one of the sections below but not both.
# Kafka with ZooKeeper:
Run the following commands in order to start all services in the correct order:
# Start the ZooKeeper service
Open another terminal session and run:
# Start the Kafka broker service
Once all services have successfully launched, you will have a basic Kafka environment running and ready to use.
# Kafka with KRaft:
Kafka can be run using KRaft mode using local scripts and downloaded files or the docker image. Follow one of the sections below but not both to start the kafka server.
Generate a Cluster UUID
Format Log Directories
Start the Kafka Server
My Top Playlists:
We start with the basics, covering what Kafka is and its key components such as producers, consumers, topics, and partitions. You'll learn about the flow of data within Kafka and explore real-world use cases where Kafka shines.
Next, we dive into practical demonstrations. Discover how to create Kafka producers efficiently and send messages both synchronously and asynchronously. Learn the nuances of sending messages with and without keys, and explore strategies for efficient message routing and consumption.
We then explore advanced topics including custom message production and consumption, handling consumer partition rebalancing with multiple consumers, and optimizing offset commitments for reliability.
Throughout the video, we emphasize best practices for error handling and discuss considerations for deploying Kafka applications outside of cloud environments or Kubernetes.
Whether you're new to Kafka or looking to deepen your understanding, this video provides actionable insights and practical examples that will accelerate your journey towards mastering Kafka with Spring Boot.
Don't forget to like, comment, and subscribe for more tutorials on Spring Boot, Kafka, and other cutting-edge technologies!
START THE KAFKA ENVIRONMENT:
NOTE: Your local environment must have Java 8+ installed.
Apache Kafka can be started using ZooKeeper or KRaft. To get started with either configuration follow one of the sections below but not both.
# Kafka with ZooKeeper:
Run the following commands in order to start all services in the correct order:
# Start the ZooKeeper service
Open another terminal session and run:
# Start the Kafka broker service
Once all services have successfully launched, you will have a basic Kafka environment running and ready to use.
# Kafka with KRaft:
Kafka can be run using KRaft mode using local scripts and downloaded files or the docker image. Follow one of the sections below but not both to start the kafka server.
Generate a Cluster UUID
Format Log Directories
Start the Kafka Server
My Top Playlists:
 0:51:29
0:51:29
 0:56:49
0:56:49
 1:37:44
1:37:44
 1:31:08
1:31:08
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 1:19:36
1:19:36
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 4:50:16
4:50:16
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:21:35
0:21:35
 0:25:59
0:25:59
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:18:48
0:18:48
 0:28:00
0:28:00
 1:25:57
1:25:57
 0:20:39
0:20:39
 0:14:07
0:14:07
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:42:59
0:42:59
 1:35:50
1:35:50
 1:44:25
1:44:25
 0:07:35
0:07:35
 0:26:26
0:26:26
 0:13:04
0:13:04